What’s RF Coaxial Cable?
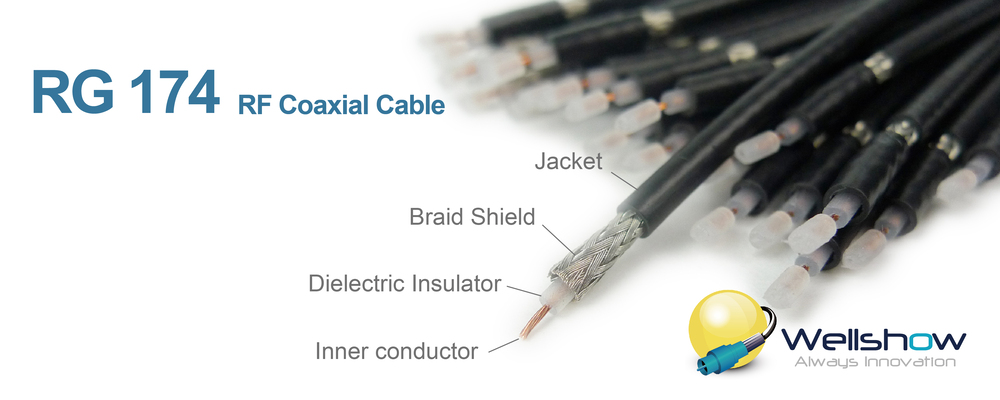
Coaxial cable (coax cable) is an electrical cable with inner conductor, dielectric insulator, shielding (Outer conductor) and jacket. Coaxial cables play a crucial role in signal transmission for radio frequency (RF) applications and are typically terminated with RF connectors such as SMA, SMB, TNC, N, FME, MCX, and MMCX. These are used to create RF coaxial cable assemblies that connect modules and antennas.
The choice of coaxial cable affects frequency performance, flexibility, strength, attenuation, power capability, and cost. The materials used in the inner structure determine the performance of the coaxial.
The inner conductor may be solid or stranded. A solid conductor has lower loss, while a stranded conductor is more flexible. For high-frequency performance, the inner conductor may be silver-plated. To reduce costs, the inner conductor may be made of copper-clad steel. The size of the inner conductor is also important for lower loss; a larger conductor allows for quick and smooth signal transmission and is a better choice for longer lengths.
The insulator or dielectric wraps around the inner conductor and may be made of solid plastic, foam plastic, or air with spacers. Common materials include PE, Foamed PE, FEP and PTFE.
The Outer Conductor or Shielding can be made of braided copper wire, braided aluminum wire, or a solid metal tube. For better shielding performance, some coaxial cables are designed with double-layered wire braid or aluminum or copper foil covered by one layer of wire braid. The density of the braided wire determines the shielding performance. Sometimes, the braid is silver-plated, tin-plated, or just bare copper.
The Jacket can be made from various materials such as PVC, PFA, FEP, and PE. A PE jacket can be used outdoors for temperature resistance, while PVC is more flexible and commonly used indoors.
